Hey ❗❗❗ I come back, and two things come with me:
- The first one, a new data structure
- The second, a new music band that I really like, And the posts about this new data structure will follow the vibe I get from this band 🥥🏝️🐠🌊.
So let ’s get to it!
Doubly linked list #
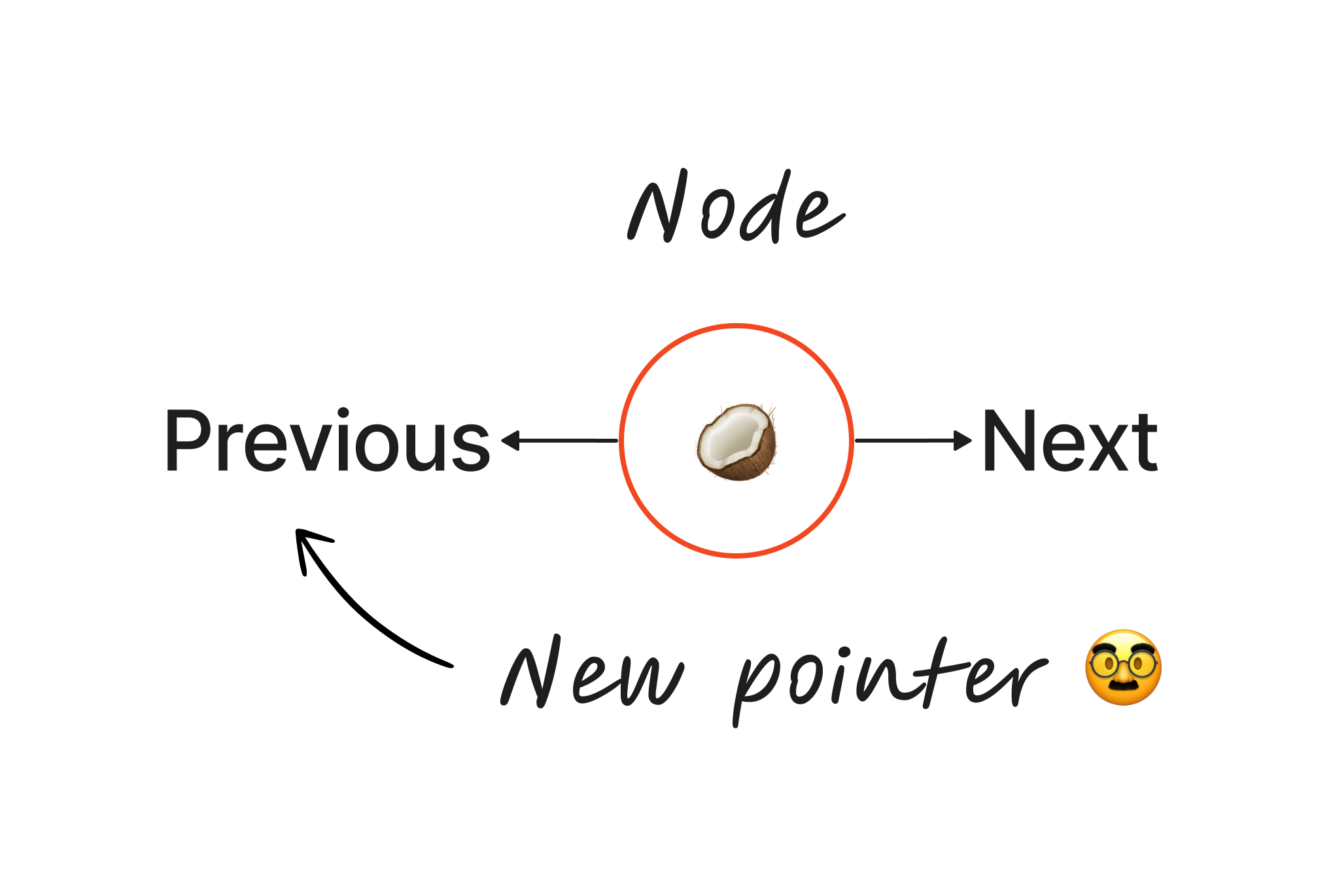
So, what is a doubly linked list, basically is a bi-directional linked list. So, you can traverse it in both directions. Unlike singly linked lists, its nodes contain one extra pointer called the previous pointer. This pointer points to the previous node 🥸.
To be honest it is tooo similar to a linked list, but this extra pointer called previous node helps us a lot to write methods for our double linked list class, we see it later on.
Node class 🏗️ #
If you remember in a previous post we already write a node class, and these node class be the base of the our current node class (we only add one attribute 🤫)
Code #
class Node:
def __init__(self, value: any) -> None:
self.value = value
self.next = None
self.prev = None
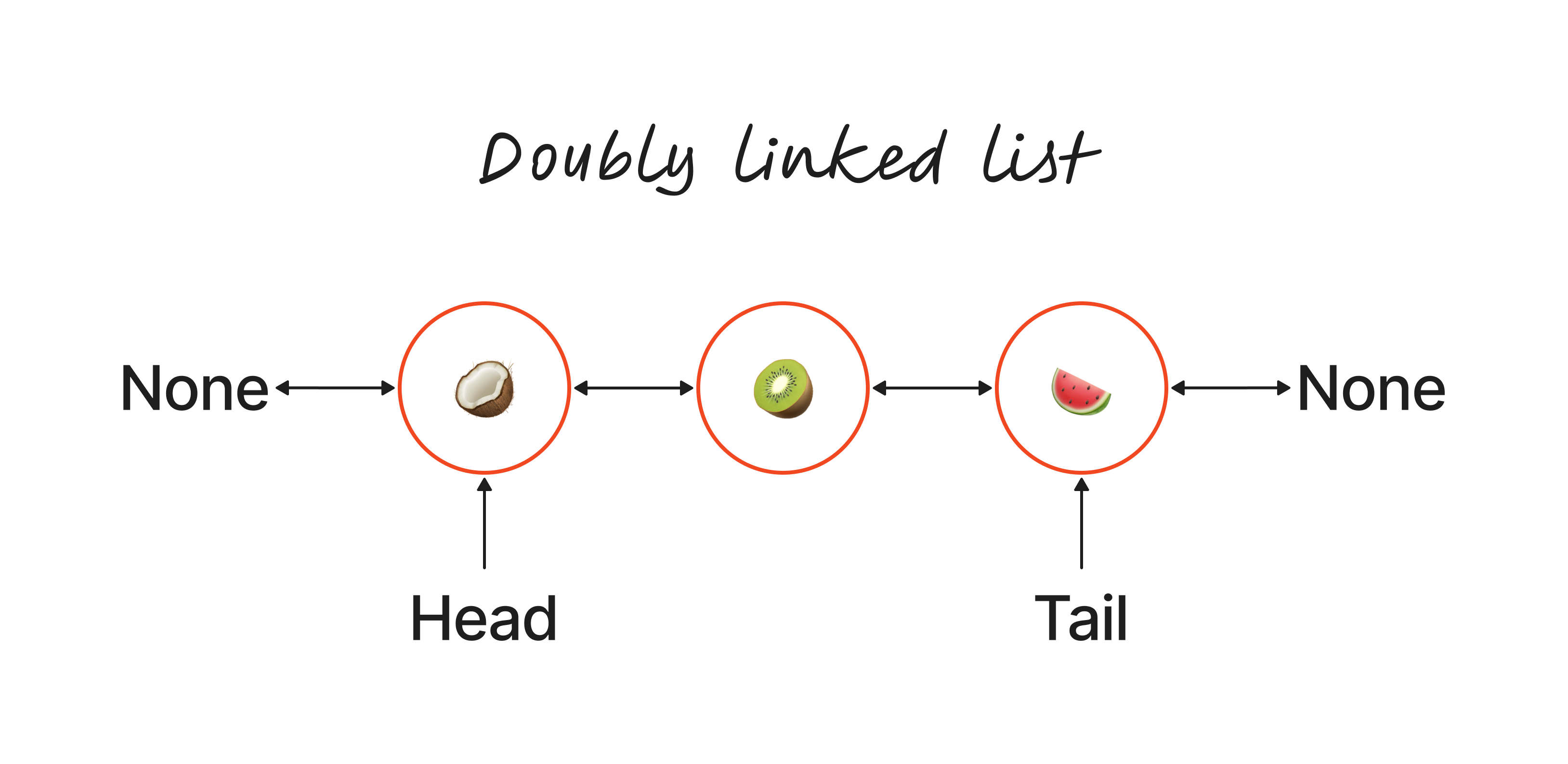
Doubly linked list class #
Constructor 🧱 #
I won’t get too complicated here, and just say that it is the same as the one used in the linked list. 😅
Code #
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self,value: any) -> None:
new_node = Node(value)
self.head = new_node
self.tail = new_node
self.length = 1
Ahhhh 🤔, I think it is a good idea to add an extra method that helps us to print our linked list, as we have also written in the linked list section
Some extra code 🪡 #
class LinkedList:
# previous code
def print_list(self) -> None:
temp = self.head
while temp is not None:
print(temp.value)
temp = temp.next
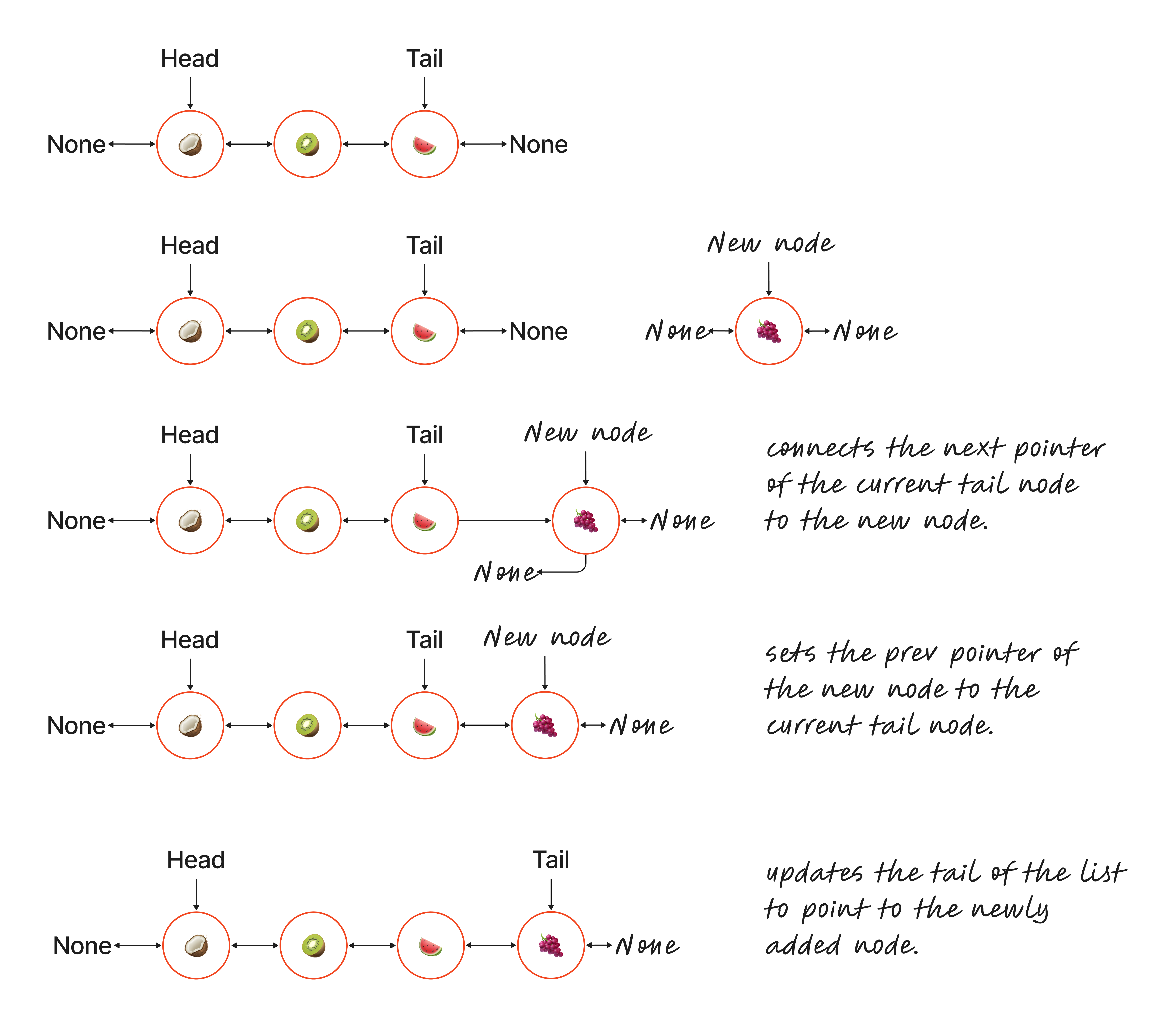
Append method #
The append method adds a new node to the end of the linked list.
Breakdown of the steps:
-
Creates a new node: It instantiates a new
Nodeobject, passing the givenvalueas an argument to store within the node. -
Handles an empty list:
- If the list is currently empty (
self.head is None), it sets both the head and tail of the list to point to the newly created node. This establishes the starting point of the list.
- Appends to a non-empty list:
- If the list already has nodes:
- It connects the
nextpointer of the currenttailnode to the new node. - It sets the
prevpointer of the new node to the currenttailnode. - It updates the
tailof the list to point to the newly added node. This ensures the list’s end is correctly maintained.
- Increments length: It increases the
lengthattribute of the list, keeping track of the number of nodes.
Code #
class DoublyLinkedList:
# previous code
def append(self, value: any):
"""
It adds a new node containing a specified value to the end of a doubly linked list
Args
Value: the data that will contain the new node
Return
None
"""
new_node = Node(value)
if self.head is None:
self.head = new_node
self.tail = new_node
else:
self.tail.next = new_node
new_node.prev = self.tail
self.tail = new_node
self.length += 1
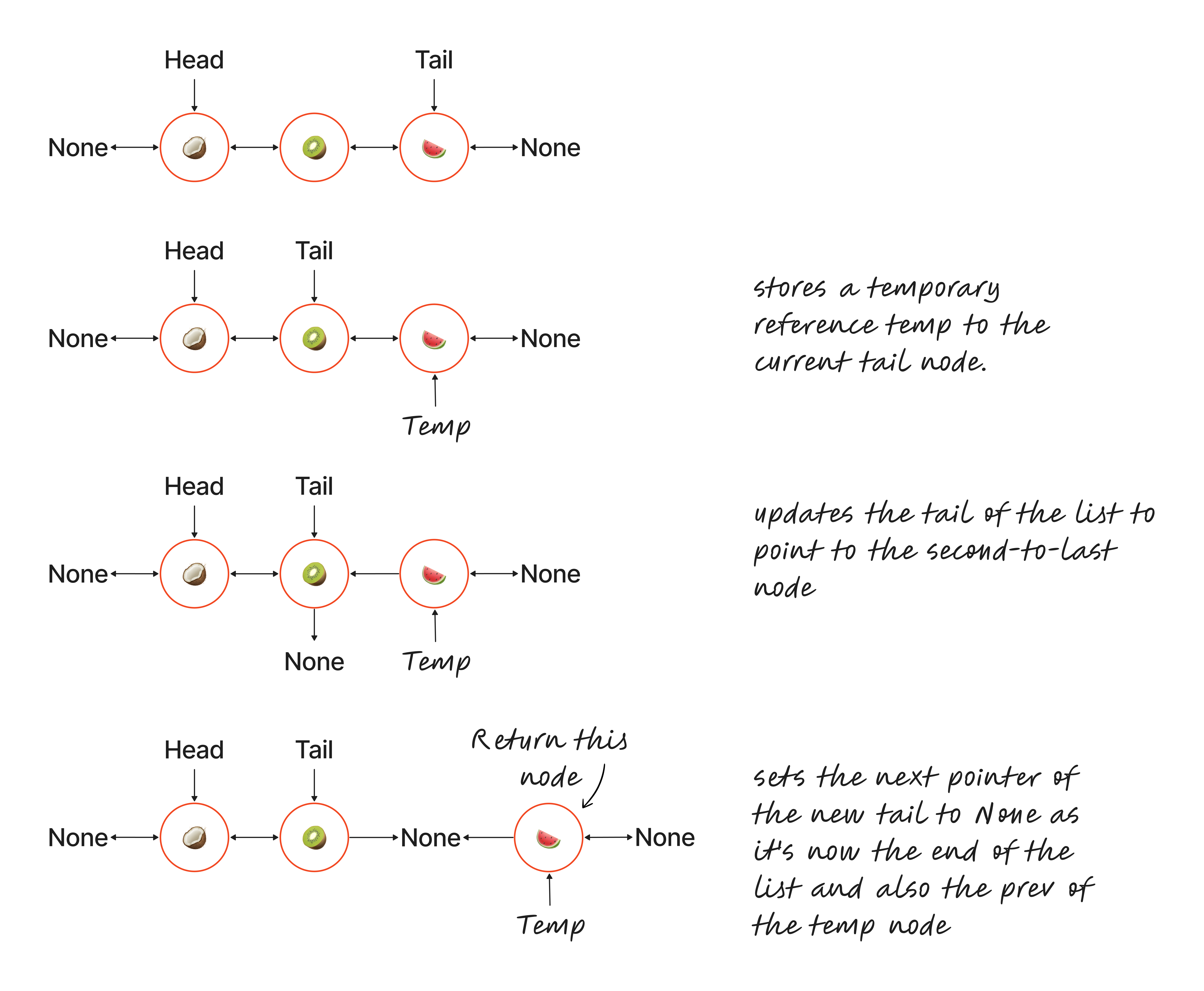
Pop method #
The pop method removes the last item of the doubly linked list and returns this node.
Steps involved:
- Checks for empty list:
- If the list is empty (
self.length == 0), it doesn’t have any elements to remove. The method returnsNoneto indicate this.
- Handles removing the single element:
- If there’s only one element in the list (
self.length == 1), it sets bothheadandtailtoNoneas there are no more nodes left.
- Removes last element from non-empty list (length > 1):
- It stores a temporary reference (
temp) to the current tail node. This is the element that will be removed. - It updates the tail of the list to point to the second-to-last node (
temp.prev). - It sets the
nextpointer of the newtailtoNoneas it’s now the end of the list. - It detaches the removed node (
temp) by setting itsprevpointer toNone. This helps avoid lingering references.
- Updates list length: It decrements the
lengthattribute to reflect the removal of a node. - Returns removed element: The method returns the temporary reference (
temp) which holds the data of the removed node.
Code #
class DoublyLinkedList:
# previous code
def pop(self) -> any:
"""
This method removes and returns the last element from a doubly linked list.
Return
None: if the doubly linked list is empty
Node: if the doubly linked list is not empty
"""
if self.length == 0:
return None
temp = self.tail
if self.length == 1:
self.head = None
self.tail = None
else:
self.tail = temp.prev
self.tail.next = None
temp.prev = None
self.length -= 1
return temp
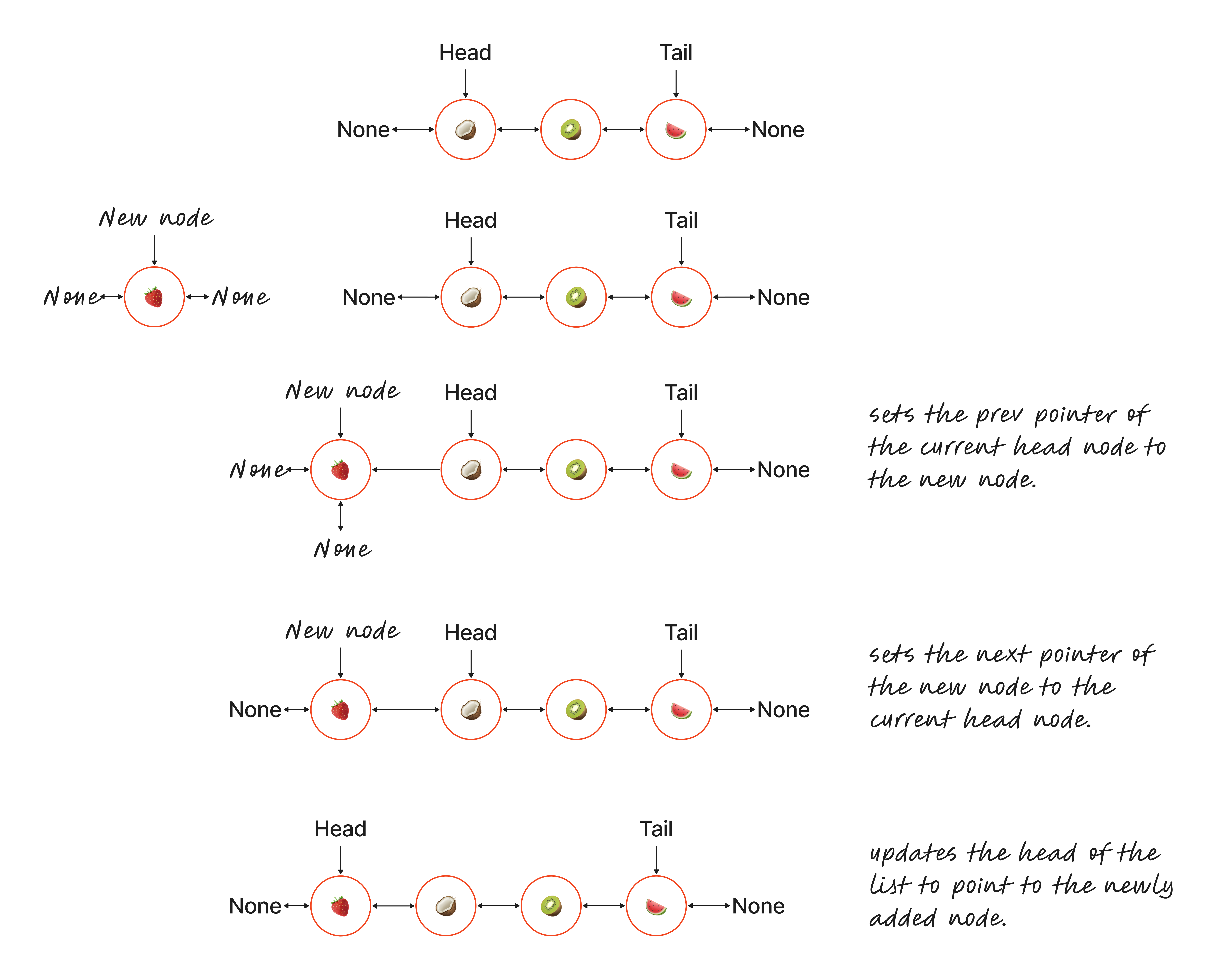
Prepend method #
The last method that will describe but not least important is the prepend method. This method adds a new node to the beginning of the doubly linked list and returns true to signal successful prepending of the new element.
Breakdown of the steps:
- Creates a new node: It creates a new
Nodeobject, storing the providedvaluewithin it. - Handles an empty list:
If the list is currently empty (
self.length == 0), it sets both head andtailof the list to point to the newly created node. This establishes the first and only element in the list. - Prepends to a non-empty list:
- If the list already has nodes:
- It sets the
prevpointer of the current head node to the new node. This creates a connection between the new node and the previous first node. - It sets the
nextpointer of the new node to the current head node. This establishes the new node as the first node in the list. - It updates the
headof the list to point to the newly added node, reflecting the new beginning.
- Increments length: It increases the
lengthattribute to account for the new node added to the list.
Code #
class DoublyLinkedList:
# previous code
"""
This method adds a new node containing a specified value to the beginning (front) of a doubly linked list
Args
Value: the data that will contain the new node
Return
bool
"""
new_node = Node(value)
if self.length == 0:
self.head = new_node
self.tail = new_node
else:
self.head.prev = new_node
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
self.length += 1
return True
The songs of the post #
Recently i watched a movie called Anatomy of a fall (and is a really good movie, I 💯 percent recommended it), and in the first minutes of the movie sound this song:
PIMP
— Bacao Rhythm & Steel Band
It was love at first hearing 👂💘.
Obviously is cover of P.I.M.P by 50 Cent.
So I decided to listen to more of this band and I really liked their tropical vibes, I recommend you to listen to them if you have the opportunity to. My favorite song is:
Bacao Suave
— Bacao Rhythm & Steel Band